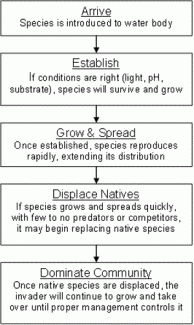
How Aquatic Species Invade
Invasive species are transported between water bodies in several ways:
- Boat traffic and boat trailers: plant fragments stuck to boats and watercraft, wrapped around motors, trailers and fishing gear and microscopic animal larvae in bilge water can move AIS between water bodies
- Bait or bait buckets: If released into the water, animals used as live bait or accidentally caught in bait buckets can become invasive species
- Aquarium and water garden disposal: pets and plants that are dumped from aquariums or water gardens into natural water bodies may end up taking over their new environments
- Planting: Individuals planting aquatic plants along their property may introduce an invasive species to that water body
- Wildlife: plant fragments or seeds snagged on waterfowl or mammals can spread invasives throughout the ecosystem
- Rivers: streams flowing out of infested lakes can spread AIS downstream throughout the watershed
Preventing the Spread of AIS
Humans are the primary reason for the rapid spread of AIS; it is important that everyone does their part to prevent the further introduction and spread of invasive species.
Steps YOU can take to prevent the spread of AIS:

- Know your surroundings. Be aware of which lakes, ponds and rivers are known to be infested with invasive species; Click here for the RI AIS distribution map
- Recognize the usual suspects. Learn to identify common aquatic invasive species in RI; Click here for a guide to identifying common aquatic invasive species
- Inspect and clean. Examine your boat and trailer before and after any use. Carefully remove any mud, plant or animal material before transporting your boat, gear and equipment.
- Allow time to dry. Clean and dry anything that came in contact with the water (boat, trailers, recreational equipment, clothing, dogs, etc.)
- Isolate and drain. Empty water from boat wells and motors far away from lakes and rivers.
- Discard into trash. Dispose any unused bait into proper garbage receptacles; do not empty bait buckets into the water.
- Prevent releases. Avoid disposing plants, fish or animals from aquariums or water gardens into local water bodies.
- Aquatic Invasive Species
- Aquatic Invasive Animals
- Aquatic Invasive Plants
- RIDEM Response
- New England Aquatic Nuisance Species Panel
- Aquatic Nuisance Species Task Force
- National Invasive Species Information Center
- USGS Nonindigenous Aquatic Species
- Protect Your Waters
- Invasive Plant Atlas of New England
Identification and Management of Aquatic Invasive Species
PDF file, about 7megabytes
Identifying Freshwater Aquatic Invasive Species in Rhode Island
PDF file, about 9megabytes
Aquatic Invaders in RI: Survey Results
PDF file, about 13megabytes
Distribution Map of Aquatic Invasive Species in RI
PDF file, about 3megabytes
Rhode Island Aquatic Invasive Species Management Plan
PDF file, about 1megabytes
2012 RI Lakes Report
PDF file, about 11megabytes
GREAT Boater Program Poster
PDF file, about 2megabytes
GREAT Boaters Program - Volunteer Handbook
PDF file, about 3megabytes
